Bits and Bytes In Hexadecimal Notation
Digital technology groups 8 bits together to form a byte. It does not very often operate with the smallest possible digital quantity.
Since 8 bits is 1 byte, therefore 8, 16 or 32 bit units are termed accordingly 1, 2 or 4 byte units. When it comes to larger range of values, like 2-byte variable: 01101001 00001101, the binary system with its 0’s and 1’s soon becomes unclear. So inorder to achieve clarity, hexadecimal system can be used. In this numbering system, each character can assume 16 different values: 0 to 9 and A to F.
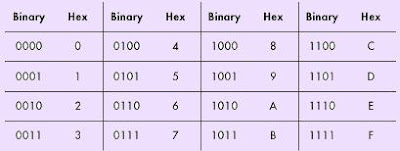 |
| Binary and hexadecimal representation of a 4-bit unit |
| Hexadecimal | Binary | |
| 0 | 0000 | |
| 1 | 0001 | |
| 2 | 0010 | |
| 3 | 0011 | |
| 4 | 0100 | |
| 5 | 0101 | |
| 6 | 0110 | |
| 7 | 0111 | |
| 8 | 1000 | |
| 9 | 1001 | |
| A | 1010 | |
| B | 1011 | |
| C | 1100 | |
| D | 1101 | |
| E | 1110 | |
| F | 1111 |

Comments
Post a Comment